East China Sea
| East China Sea | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
|||||||
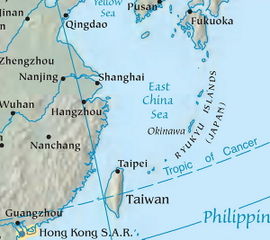
| The East China Sea, showing surrounding regions, islands, and cities | |||||||
| Chinese name | |||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 東海 or 東中國海 | ||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 东海 or 东中国海 | ||||||
|
|||||||
| Japanese name | |||||||
| Kanji | 東シナ海 | ||||||
|
|||||||
| Korean name | |||||||
| Hangul | 동중국해 or 남해 | ||||||
| Hanja | 東中國海 or 南海 | ||||||
|
|||||||
The East China Sea (Chinese: 東海) is a marginal sea east of China. It is a part of the Pacific Ocean and covers an area of 1,249,000 km² or 750,000 square miles.
Contents |
Geography
The East China Sea is bounded on the east by the Kyūshū and Ryukyu Islands, on the south by Taiwan, and on the west by mainland China. It is connected with the South China Sea by the Taiwan Strait and with the Sea of Japan by the Korea Strait; it opens in the north to the Yellow Sea.
Territories with borders on the sea (clockwise from north) include: South Korea, Japan, Taiwan and Mainland China. Max depth: 3,000 m.
Extent
The International Hydrographic Organization defines the limits of the "Eastern China Sea (Tung Hai)" as follows:[1]
On the south. The northern limit of the South China Sea [From Fuki Kaku the north point of Formosa to Kiushan Tao (Turnabout Island) on to the south point of Haitan Tao (25°25'N) and thence westward on the parallel of 25°24' north to the coast of Fukien], thence from Santyo the northeastern point of Formosa to the west point of Yonakuni Island and thence to Haderuma Sima ().
On the east. From Haderuma Sima a line including the Miyako Retto to the east point of Miyako Sima and thence to Okinan Kaku, the southern extremity of Okinawa Sima through this island to Ada-Ko Sima (Sidmouth Island) on to the East point of Kikai Sima (28°20'N) through Tanegra Sima (30°30'N) to the north point thereof and on to Hi-Saki (31'17'N) in Kyūshū.
On the north. From Nomo Saki (32°35'N) in Kyusyu to the south point of Hukae Sima (Goto Retto) and on through this island to Ose Saki (Cape Goto) and to Hunan Kan, the South point of Saisyu To (Quelpart), through this island to its western extreme and thence along the parallel of 33°17' north to the mainland.
On the west. The mainland of China.
Rivers
The Yangtze River (Chang Jiang) is the largest river flowing into the East China Sea.
Islands and reefs
- Tong Island
There is a cluster of submerged reefs in the northern East China Sea. These include:
- Socotra Rock, also called Suyan Rock or Ieodo, subject of an EEZ dispute between the People's Republic of China and South Korea.
- Hupijiao Rock (虎皮礁)
- Yajiao Rock (鸭礁)
EEZ disputes
There are disputes between China, Japan, and South Korea over the extent of their respective exclusive economic zones.
The dispute between China and Japan concerns natural gas. The People's Republic of China (PRC) recently discovered that there exists an undersea natural gas field in the East China Sea, part of the field lies within the Chinese EEZ while the remaining lies on the disputed EEZ between Japan and the PRC.

Under the United Nations' Law of the Sea, PRC claims the disputed ocean territory as its own Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) due to its being part of PRC's natural extension of its continental shelf, while Japan claims the disputed ocean territory as its own EEZ because it is within 200 nautical miles (370 km) from Japan's coast.
China has set up the Chunxiao gas field, which is located more than 4 km inside the Chinese side of the EEZ boundary claimed by Japan and is within China's own EEZ, to extract the natural gas. Japan maintains that although the Chunxiao gas field rigs are on China's side of a median line that Tokyo regards as the two sides' sea boundary, they may tap into a field that stretches into the disputed area. Japan therefore seeks a share in the natural gas resources.
The dispute between China and South Korea concerns Socotra Rock, a submerged reef on which South Korea has constructed a scientific research station. While neither country claims the rock as territory, China has objected to Korean activities there as a breach of its EEZ rights.
See also
- Geography of China
- Xihu Trough
- Geography of Japan
- Senkaku Islands (Diaoyu Islands in Chinese)
- South China Sea
References
- ↑ "Limits of Oceans and Seas, 3rd edition". International Hydrographic Organization. 1953. http://www.iho-ohi.net/iho_pubs/standard/S-23/S23_1953.pdf. Retrieved 7 February 2010.
- Note, Alexander M. Peterson "Sino-Japanese Cooperation in the East China Sea: A Lasting Arrangement?" 42 Cornell International Law Journal 441 (2009).
External links
- Kosuke Takahashi . Gas and oil rivalry in the East China Sea Asia Times Online. July 27, 2004.
- Chinese submarine enters Japanese waters. Wikinews. November 18, 2004. Retrieved March 7, 2006.
- Oil and gas in troubled waters The Economist. October 6, 2005.
- J Sean Curtin. Stakes rise in Japan, China gas dispute Asia Times Online. October 19, 2005.
- Chinese Suyan Rock community
- Alexander M. Peterson's 2009 Note in the Cornell International Law Journal detailing the dispute, clarifying the legal impact of the 2008 Sino-Japanese arrangement to cooperate in the East China Sea, and proposing increased Sino-Japanese cooperation.
|
|||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||